How To Get Rid of Moles on Skin: Is It Safe?
If you have any moles, you may have considered removing them due to their appearance. And while they may not be concerning on their own, they could potentially become cancerous over time. As a result, you should be conducting monthly self-checks of your moles and visiting a dermatologist annually for a professional examination.
What Are Moles?
While you may know what moles are, generally speaking, you probably don’t know what they actually are. As a result, moles can appear as brown, tan, black, red, blue, or pink in color.
Additionally, moles are typically oval or round in shape and may be smooth, wrinkled, flat, or raised. They may also have hair growing from them. In terms of size, moles are usually quite small — less than a quarter of an inch in diameter or smaller than the size of a pencil eraser.
Moles are quite common. In fact, most people have anywhere from 10 to 40 moles on their bodies. Most moles develop during childhood and adolescence — before the age of 25. Contrary to popular belief, moles may not be permanent. Instead, they have an average life cycle of about 50 means — meaning that, as the years pass, moles can slowly disappear over time.
What Causes the Development of Moles?
While moles are common, some people are more prone to them than others. Genetic factors may contribute to the development of moles. So if your parents or grandparents have a large number of moles, you’re more likely to experience the same thing. Sun exposure also contributes to the development of moles. So if you live in a very sunny climate or spend long hours outdoors in the sun, you’re more likely to develop moles as a result.
What Are the Different Types of Moles?
Contrary to popular belief, not all moles are the same. In fact, there are several different types that you should be aware of, including:
- Common nevi: This type of mole is the most common — presenting as a small skin growth with a distinct edge that may be pink, tan, or brown in color.
- Congenital nevi: This type of mole is present at birth and is relatively aware — only occurring in about 1% of people. While these moles aren’t usually concerning, they carry a slightly higher risk of developing into skin cancer.
- Dysplastic nevi: This type of mole is larger than a common mole and has an irregular shape with an uneven color. They typically present with dark brown centers and lighter edges with uneven borders. Like congenital nevi, dysplastic nevi carries a slightly higher risk of developing into skin cancer.
When Should You Be Concerned About a Mole?
Most moles should not be a cause for concern. However, it’s still important to monitor your skin for the appearance of new moles and changes in existing moles as these could be indications of skin cancer.
If you have any concerns about the appearance of your moles, you should consult with a dermatologist who will be able to tell you if it is potentially cancerous or not.
Here are some things that you should look out for based on these “ABCDE” guidelines:
- Asymmetry: If the mole is asymmetrical — with one side not matching the other — you should get your mole checked out.
- Border: If the mole has an uneven border with edges that are ragged, blurred, or irregular, you should get your mole checked out.
- Color: If the mole is an uneven color with varying shades of tan, brown, black, blue, white, or red, you should get your mole checked out.
- Diameter: If the diameter of the mole is larger than the size of a pencil eraser, you should get your mole checked out.
- Evolution: If you have noticed that the mole is changing in size, shape, or color, you should get your mole checked out.
Additionally, you should have your mole checked out if it is bleeding, oozing, itching, or is painful. Pay special attention to areas of the skin that frequently experience sun exposure, including the hands, chest, neck, face, ears, legs, and back.
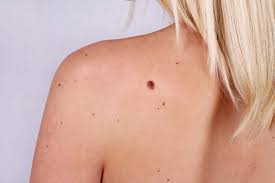
Can Moles Be Safely Removed?
The best way to remove a mole is by going to a dermatologist to have it professionally and safely removed.
This procedure involves the use of some type of numbing mechanism so that you can’t feel it and usually has little to no recovery time depending on the size of the mole and the removal method.
There are three different techniques that dermatologists typically use to remove a mole:
- Shave biopsy: This technique uses a razor blade to shave off the mole and the skin surrounding it.
- Punch biopsy: This technique uses a punch tool that is then placed over the mole and effectively “punches” it out of the skin.
- Scalpel removal: This technique uses a scalpel to remove the mole and the skin surrounding it. Stitches are then used to sew up the wound and help it heal.
After removal, you will need to keep a bandage on the removal site for a few days. Make sure to follow the care instructions provided to you by your dermatologist.
How To Get Rid of Moles on Skin
If you’re hesitant to have your mole cut off by a professional, there are some home remedies that are worth trying.
Here are some natural and gentle methods to potentially remove or lighten the appearance on your skin:
- Apple cider vinegar
- Garlic
- Baking soda
- Castor oil
- Tea tree oil
- Frankincense oil
- Flaxseed oil
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Aloe vera
- Banana peel
If you’re hesitant to have your mole cut off by a professional, there are some home remedies that are worth trying. However, if your mole presents any of the ABCDE issues, then you need to get it checked and removed by a dermatologist. Additionally, cutting off or taking any drastic action to remove the mole on your own is never recommended as it may cause an infection.
- Keywords: Moles, Skin
- miracleadmin