Eczema on the Face
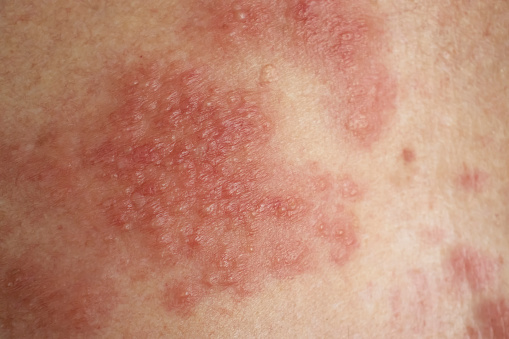
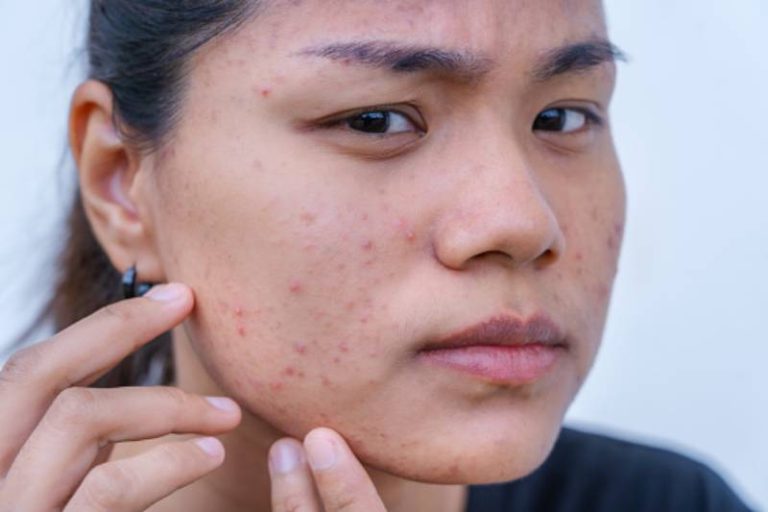
Eczema is a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. When eczema affects the face, it can be particularly distressing because it is a highly visible area of the body.

Here are some tips to manage eczema on the face:
- Keep your skin moisturized: Apply a moisturizer to your face at least twice a day. Look for a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer that is specifically formulated for eczema-prone skin.
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that can make your eczema worse. Common triggers include stress, certain foods, exposure to harsh chemicals, and extreme weather conditions.
- Use gentle skincare products: Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers and avoid using harsh soaps or scrubs. Be gentle when cleansing and pat your face dry with a soft towel.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching can worsen eczema symptoms and increase the risk of infection. If you feel the urge to scratch, try applying a cold compress or a moisturizer instead.
- Consult with a dermatologist: If your eczema is severe or doesn’t respond to over-the-counter treatments, consult with a dermatologist. They can recommend prescription-strength creams or other treatments that may be more effective for you.
Remember that eczema on the face can be managed with proper care and attention. With the right treatment and self-care, you can reduce your symptoms and improve the appearance of your skin.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes red, dry, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. It is a type of allergic reaction that affects the skin’s ability to retain moisture, making it more susceptible to irritants and allergens.
Eczema can occur at any age, but it usually starts in childhood and affects around 10-20% of infants and young children. In many cases, eczema improves or disappears by adulthood, but for some, it can continue into adulthood.

The exact cause of eczema is not yet known, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema often have a family history of the condition or other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever.
The symptoms of eczema can vary in severity and can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as stress, certain foods, harsh soaps or detergents, cold weather, and dry air. While there is no cure for eczema, treatment options such as moisturizers, prescription creams, and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Common Eczema Triggers
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that can be triggered by a variety of factors. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Here are some common eczema triggers:
- Allergens: Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger eczema symptoms. It’s important to identify and avoid allergens that affect you.
- Irritants: Irritants such as soaps, detergents, and cleaning products can irritate the skin and trigger eczema. Use gentle, fragrance-free products that are specifically formulated for sensitive skin.
- Stress: Stress can trigger eczema symptoms, so it’s important to practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and exercise.
- Weather: Changes in weather, particularly cold and dry weather, can trigger eczema. Moisturize your skin regularly and avoid extreme temperature changes.
- Foods: Certain foods such as dairy, soy, nuts, and wheat can trigger eczema in some people. Keep a food diary to identify and avoid foods that trigger your symptoms.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy and menopause, can trigger eczema symptoms.
- Scratchy clothing: Scratchy or tight clothing made from materials such as wool or polyester can irritate the skin and trigger eczema.
By identifying and avoiding these common eczema triggers, you can help manage your symptoms and prevent flare-ups. It’s important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific triggers and needs.
How Do You Treat Eczema?
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that has no cure, but it can be effectively managed with proper treatment. The treatment for eczema typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, self-care, and medication. Here are some common treatments for eczema:
- Moisturizers: Using a good quality moisturizer helps to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness, which can trigger eczema. Look for a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer that is specifically formulated for eczema-prone skin.
- Topical corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory creams or ointments that can be used to reduce redness and inflammation associated with eczema. They are available in varying strengths and can be used for short-term or long-term use under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors: These are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory creams that can also be used to reduce redness and inflammation. They are particularly useful for treating eczema on the face and in sensitive areas.
- Wet wraps: Wet wraps can be used to soothe and moisturize eczema-prone skin. They involve wrapping a layer of damp gauze or bandages over the skin after applying moisturizer or medication.
- Phototherapy: Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under the supervision of a healthcare provider. It can be an effective treatment for moderate to severe eczema.
- Oral medication: In severe cases, oral medications such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed by a healthcare provider.
In addition to these treatments, it’s important to avoid triggers that can make eczema worse and practice good self-care such as taking lukewarm baths, wearing soft cotton clothing, and avoiding scratching. By working with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, you can effectively manage your eczema symptoms and improve the health and appearance of your skin.
- Keywords: Eczema, face, Skin
- miracleadmin