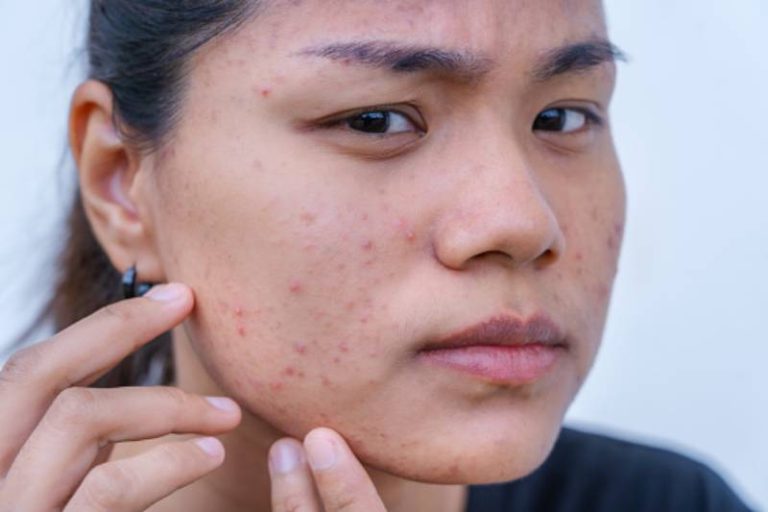
Acne marks vs acne scars: How to tell the difference
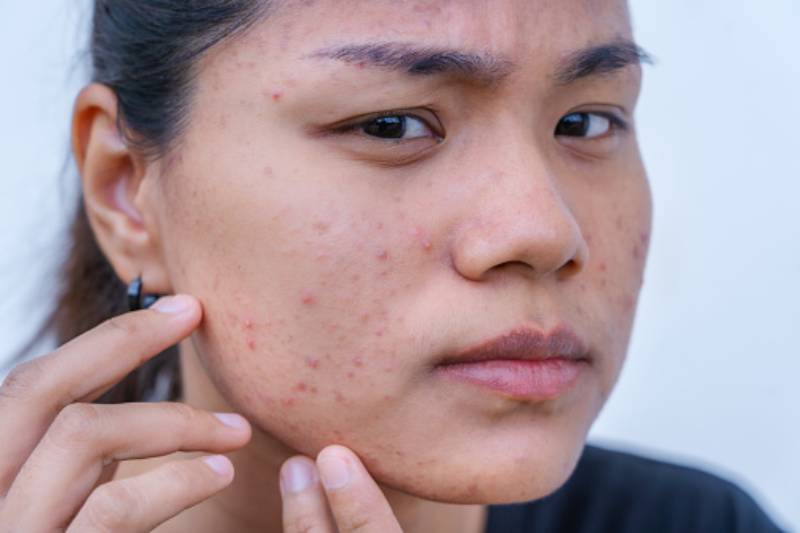
Acne marks and acne scars are two common types of skin discoloration that can occur as a result of acne. While they may look similar, there are some differences between the two.
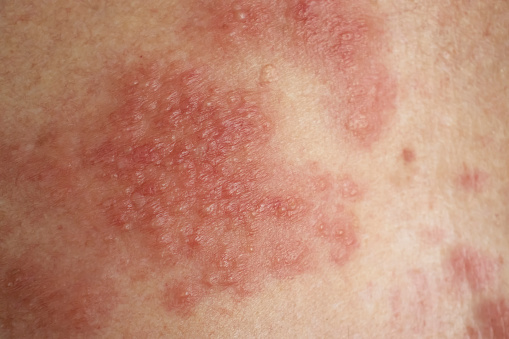
Acne marks, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), are flat, dark spots that occur after an acne lesion has healed. They are caused by an overproduction of melanin in response to inflammation. PIH usually fades on its own over time, but it can take several months to a year or more to fully disappear.
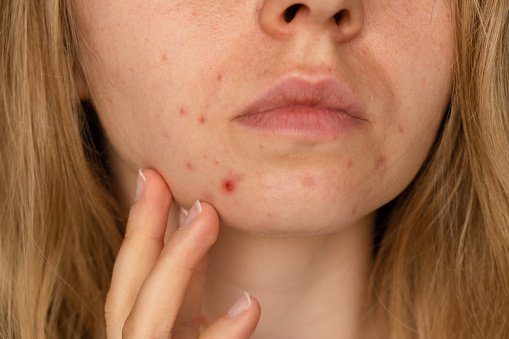
Acne scars, on the other hand, are permanent indentations or raised areas on the skin that result from damage to the collagen fibers during the healing process. There are several types of acne scars, including:
- Ice pick scars: deep, narrow scars that form pits in the skin.
- Boxcar scars: broad, flat depressions with sharp, defined edges.
- Rolling scars: broad, shallow depressions with a wavy texture.
- Hypertrophic scars: raised, thick scars that form above the skin’s surface.
To determine whether a skin discoloration is an acne mark or an acne scar, you can try the following:
- Check the texture of the skin: Acne marks are usually flat, while acne scars are either indented or raised.
- Check the color: Acne marks are usually dark brown or red, while acne scars may be a different color than your skin tone, such as white or pink.
- Observe the duration: Acne marks typically fade on their own over time, while acne scars are usually permanent.
If you’re unsure whether a skin discoloration is an acne mark or an acne scar, it’s best to consult with a dermatologist, who can provide a professional diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Acne Marks
Acne marks, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), are dark spots or discoloration on the skin that can occur after an acne breakout. They are caused by inflammation and injury to the skin, which triggers an overproduction of melanin in that area.
There are several ways to treat acne marks, including:
- Topical treatments: Over-the-counter or prescription creams or gels that contain ingredients such as retinoids, vitamin C, or hydroquinone can help lighten and reduce the appearance of acne marks.
- Chemical peels: A dermatologist can perform a chemical peel, which involves applying a solution to the skin to remove the top layer and promote cell turnover. This can help reduce the appearance of acne marks.
- Microdermabrasion: This is a non-invasive procedure that uses a machine to exfoliate the outer layer of skin and promote new skin growth. It can help reduce the appearance of acne marks and improve overall skin texture.
- Laser treatment: Certain types of lasers can target and break down the pigment in acne marks, leading to a reduction in their appearance.
- Sun protection: Wearing sunscreen and avoiding sun exposure can help prevent further darkening of acne marks.
It’s important to note that treating acne marks can take time and patience. It’s also important to address the underlying acne to prevent new marks from forming. Consult with a dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan for your specific case.
Acne Marks vs Acne Scars
Acne marks and acne scars are two different skin conditions that can occur after an acne breakout. While they may look similar, they differ in their causes and severity.
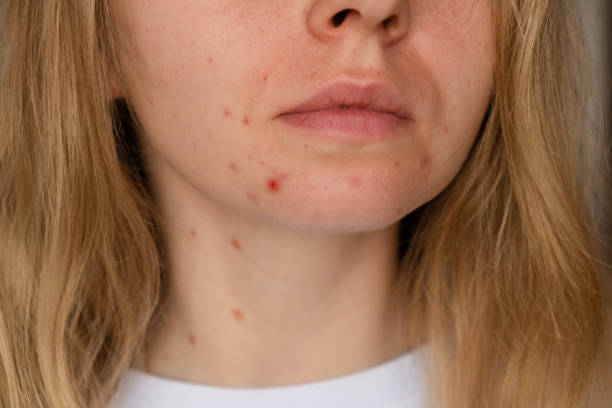
Acne marks, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), are flat, dark spots or discoloration on the skin that can occur after an acne breakout. They are caused by an overproduction of melanin in the affected area due to inflammation and injury to the skin. Acne marks typically fade over time and can be treated with topical creams, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser treatment, or sun protection.
Acne scars, on the other hand, are more severe and permanent indentations or depressions in the skin that result from the healing process of severe acne. They are caused by the formation of fibrous tissue to repair the damage caused by acne. Acne scars can be classified into different types, including ice pick scars, boxcar scars, and rolling scars. Acne scars are more difficult to treat than acne marks and may require more invasive treatments such as dermal fillers, microneedling, or laser resurfacing.
It’s important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
- Keywords: acne
- miracleadmin